Blockchain technology is a database system that enables transparent information sharing across a network. It serves as a common, immutable ledger for recording transactions between various parties and can register any type of asset that moves within a business network’s supply chain.
Unlike a traditional database, with a blockchain, the data once set cannot be tampered with, offering high levels of trust and security.This makes it a perfect fit for businesses requiring the validation of transactions or the monitoring of the flow of assets such as goods, money, or even data.
The more that industries show its potential, the more the blockchain is a game-changer to the storage, management, and protection of information. In this blog, we are going to get some gist of what blockchain technology is and how it’s changing the conventional methods of our world.
Defining Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital record of transactions from numerous computers, allowing security, transparency, and immutability. It replaces the centralized party with a network of nodes that verify and record transactions. Transactions such as this are grouped into a so-called “block” and added successively to its chain, therefore creating a secure and chronological record. Unique in the fact that each transaction is transparent to the public, blockchain technologies are trustworthy and virtually impossible to tamper with once the record is finalized.
On this idea, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have been founded, but blockchain goes instead far beyond Bitcoin into many other applications: supply chain management, and healthcare. Understanding the core function of blockchain is integral to realizing why it is considered a revolutionary tool in industries that hold security and efficiency dear.
A Brief History of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has rapidly evolved since the time of its origination. A glimpse into its evolution follows:
- Late 1970s: Ralph Merkle, a computer scientist, patented Hash trees, known as Merkle trees, for linking blocks of data with cryptography-a fundamental behind blockchain.
- Late 1990s: Using Merkle trees, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta developed a system that could record document timestamps impervious to tampering; this was the first known historical application of blockchain.
- First Generation (2008 – Bitcoin): Satoshi Nakamoto defined blockchain technology in modern times by the creation of Bitcoin, a fully decentralized ledger recording 1 MB blocks of Bitcoin transactions that lay the bedrock for every blockchain out there.
- Second Generation (Smart Contracts): Soon after, it dawned on developers that blockchains could have applications other than digital currencies. The introduction of smart contracts by Ethereum allowed automated agreement execution to broaden the horizons of blockchain.
- Third Generation-The Future: In continuation, blockchain keeps on evolving to solve scalability and opens endless opportunities for all industries of the world as more and more applications are found and implemented.
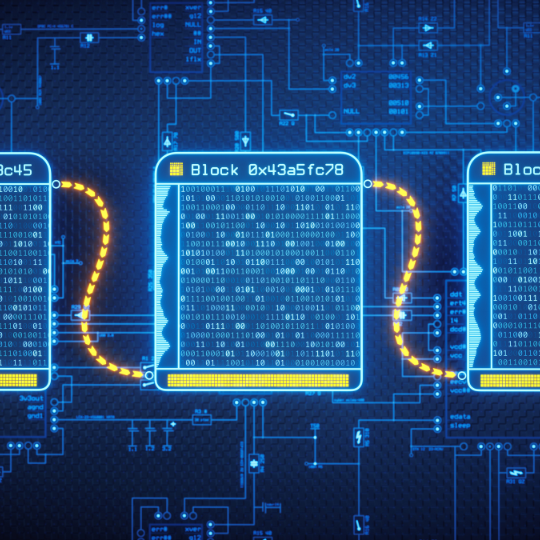
How It Actually Works?
All that blockchain is is a distributed ledger. Its data is kept in “blocks” that are connected chronologically to form a “chain”. Each new block contains a set of data and is connected to the previous block. Contrary to traditional systems, which are controlled by a central authority, blockchain relies on a network of nodes-essentially, computers-that validate and verify new data through a consensus mechanism. Before the block is added, most nodes must agree with the validity of that block.
This decentralized verification makes blockchain very secure. The transactions are encrypted; therefore, for transactions to be approved, nodes have to solve some difficult mathematical puzzles that ensure integrity to the data and, hence, tamper-proof information.
When the majority of nodes reaches consensus, then the block is added to the chain and the ledger updated on all nodes. The structure of the blockchain makes it practically impossible to change any of its past data. Secondly, nodes, in some cases referred to as miners, are incentivized for their work in the verification of the transactions.
For example, miners in systems such as Bitcoin are rewarded with freshly baked cryptocurrency. This cocktail of decentralized verification, cryptography, and incentivization secures a sound and robust data storage and management system.
Types of Blockchain Networks
There exist different types of blockchain networks to serve various needs.
- Public Blockchain Networks: These are permissionless and open, whereby anyone can join, read, and write data, and validate it. Public blockchains give a lot of priority to decentralization and transparency. This finds its most common use in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Private Blockchain Networks: In contrast to public blockchain networks, these are controlled access and, thus, partially decentralized because they are controlled by an organization. The organization determines participant roles. Ripple is a digital currency exchange network and an example of a private blockchain.
- Hybrid blockchain networks: This shall implement properties from both public and private blockchains: organizational control over who can access certain data and remaining information being made available publicly. Examples are hybrid blockchains that allow the use of smart contracts for making private transactions publicly verifiable, achieving a balance between transparency and privacy.
- Consortium Blockchain Networks: This is a network that is controlled by a preselected group of organizations and suits industries in which collaboration is key. An example is the consortium of the Global Shipping Business Network that fosters cooperation and digitalization within the maritime industry.
Applications & Features of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a technology that cuts across all industries with its various uses. Most popular, it’s often defined as the Certificate of Choice for cryptocurrency, anchored with digital coins like bitcoin, ethereum etc. However, there are advancements in blockchain technology that include traditional idea of banking but helps in faster exchange of local currencies without the use of intermediaries.
Additionally, these systems assist with asset transfers or modifications, securing the transfer of ownership even of physical real estate assets or digital NFTs within seconds. What is more, the efficiency is taken a notch higher by smart contracts that carry out certain actions upon disposition of specified conditions.
Concerning supply chain management, blockchain helps in tracing and locating products in case of defects that concern the product’s journey. While the features that distinguish a distributed ledger technology include decentralization, immutability and consensus. Even though no one organization should manage the complete network, decentralization a body by its nature restricts this. Immutability pertains to the preservation of records so that they cannot be altered for any reason and under any circumstances.
Likewise, consensus mechanisms guarantee the credibility of the information whereby in a majority represented in new transaction information has to vote and approve the new transaction information. These characteristics combined enable blockchain technology to be secure and flexible for use in different industries.
Future Prospects
Like the internet, blockchain technology is still in its infancy even though it presents many exciting possibilities. It still cannot achieve full-scale operations due to a combination of technological issues, mainly energy consumption and the maximum number of deals per second that can be completed at one time, and ideological doubts. However, as authorities and regulatory bodies continue to improve their policies, blockchain will become more widely accepted and creatively applied.
The user appreciates that a portion of the work entails a dedication to comprehending that, in line with the expansion of the internet, blockchain has the potential to transform the way we make purchases and transact with one another online. Still, some parts have already been worked on. Today’s blockchain investors are investing in decentralized systems that will disrupt all industries in the near future.